Enterprise and entrepreneurship, though often used interchangeably, represent distinct concepts in the business realm. In this exploration, we delve into the nuances that set them apart and examine their symbiotic relationship.
Understanding the dynamics of enterprise and entrepreneurship is crucial in navigating the complexities of the business world. While both contribute to economic growth, they operate on different planes, each with its unique characteristics and functions.
Table of contents
Defining Enterprise
An enterprise, in its broadest sense, refers to an organization or venture engaged in commercial, industrial, or professional activities. These entities range from multinational corporations to small local businesses, encompassing a diverse array of industries.
Entrepreneurship
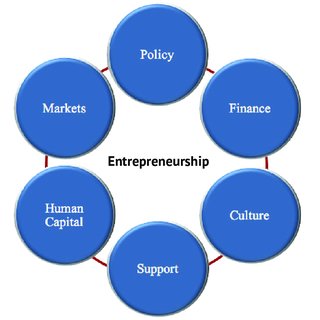
Entrepreneurship, on the other hand, is the embodiment of innovation and risk-taking. Entrepreneurs are individuals who create and manage businesses, bringing novel ideas to fruition. They possess a distinctive set of traits, including vision, resilience, and adaptability.
Distinguishing Factors
While enterprises provide stability and structure, entrepreneurship thrives on dynamism and creativity. The key difference lies in the approach to risk and innovation. Enterprises focus on optimizing existing processes, whereas entrepreneurs embrace uncertainty, seeking opportunities for groundbreaking developments.
| Factor | Enterprises | Entrepreneurship |
| Approach to Risk | Mitigation and risk reduction through careful planning and established processes. | Embracing and managing uncertainty, viewing risk as an opportunity for growth and innovation. |
| Innovation Focus | Incremental improvements, optimizing existing processes for efficiency and stability. | Groundbreaking and disruptive innovations, actively seeking new and unexplored opportunities. |
| Structure and Stability | Emphasis on organizational hierarchy, established procedures, and long-term stability. | Flexible and adaptable structures, open to rapid changes to meet evolving market demands. |
| Decision-Making Speed | Generally slower decision-making processes, involving multiple levels of approval. | Quick and agile decision-making, with the ability to adapt rapidly to changing circumstances. |
| Goal Orientation | Primarily focused on maintaining and improving current market positions and profitability. | Driven by a desire to create and capitalize on new market opportunities and trends. |
Enterprise in Action
Examining successful enterprises reveals a commitment to efficiency, scalability, and market dominance. Companies like Apple and Amazon exemplify how enterprises become industry leaders through strategic planning, resource management, and continuous improvement.
Entrepreneurs, such as Elon Musk and Oprah Winfrey, illustrate the transformative power of individual vision. Their ventures, marked by innovation and a willingness to challenge the status quo, showcase the impact of entrepreneurship on shaping industries.
Common Misconceptions
To clarify misconceptions, it’s essential to recognize that enterprises can foster entrepreneurial spirit within their structures. Simultaneously, not all entrepreneurs operate in startups; many bring entrepreneurial thinking to established organizations.
Challenges in Both Arenas
Enterprises grapple with maintaining relevance in rapidly changing markets, while entrepreneurs face the uphill battle of turning innovative ideas into sustainable businesses
Market Dynamics:
- Rapid changes in market trends and consumer preferences.
- Globalization leads to increased competition and diverse market demands.
Technology Evolution:
- Constant advancements require enterprises to adapt and integrate new technologies.
- Balancing legacy systems with emerging technologies for seamless operations.
Regulatory Compliance:
- Navigating complex and evolving regulatory landscapes.
- Ensuring compliance with industry standards and legal requirements.
Customer Engagement:
- Building and maintaining meaningful connections with customers.
- Addressing the shift towards digital platforms and changing communication channels.
Adaptability and Growth
The ability to adapt to evolving market conditions is crucial for both enterprises and entrepreneurs. While enterprises may implement incremental changes, entrepreneurs often navigate uncharted territories, relying on agility and creativity for growth.
Global Impact
The influence of enterprise and entrepreneurship extends beyond individual businesses. On a global scale, these concepts shape economies, drive technological advancements, and contribute to societal progress.
Future Trends
As we look ahead, the landscape of enterprise and entrepreneurship is evolving. Trends such as remote work, sustainable business practices, and digital transformation are shaping the future of both established businesses and innovative startups.
Conclusion
In conclusion, recognizing the distinct attributes of enterprise and entrepreneurship is fundamental in navigating the ever-changing business terrain. The intertwined nature of these concepts highlights the importance of embracing both stability and innovation for sustained success.
Readmore:
Which of the Following Factors Does not Influence Entrepreneurship Growth?
Entrepreneurship Development Cycle
Entrepreneurship as a Career Option
What is Creativity in Entrepreneurship
Frequently Asked Questions
No, many entrepreneurs bring their innovative thinking to established enterprises, contributing to their growth and adaptability.
Enterprises can encourage a culture of innovation, provide resources for creative projects, and establish partnerships with startups.
Entrepreneurs often grapple with funding constraints, market uncertainty, and the need to continuously innovate to stay competitive.
A comprehensive understanding of both concepts equips future business leaders with the skills and mindset necessary for success in diverse business environment

