Entrepreneurship and technopreneurship both navigate the realms of innovation, business, and creation. Yet, they diverge in fundamental ways that shape their approaches, goals, and impacts on industries and economies. Understanding the nuances between these two concepts unveils distinct paths and mindsets in the world of business.
Table of contents
Defining Entrepreneurship and Technopreneurship
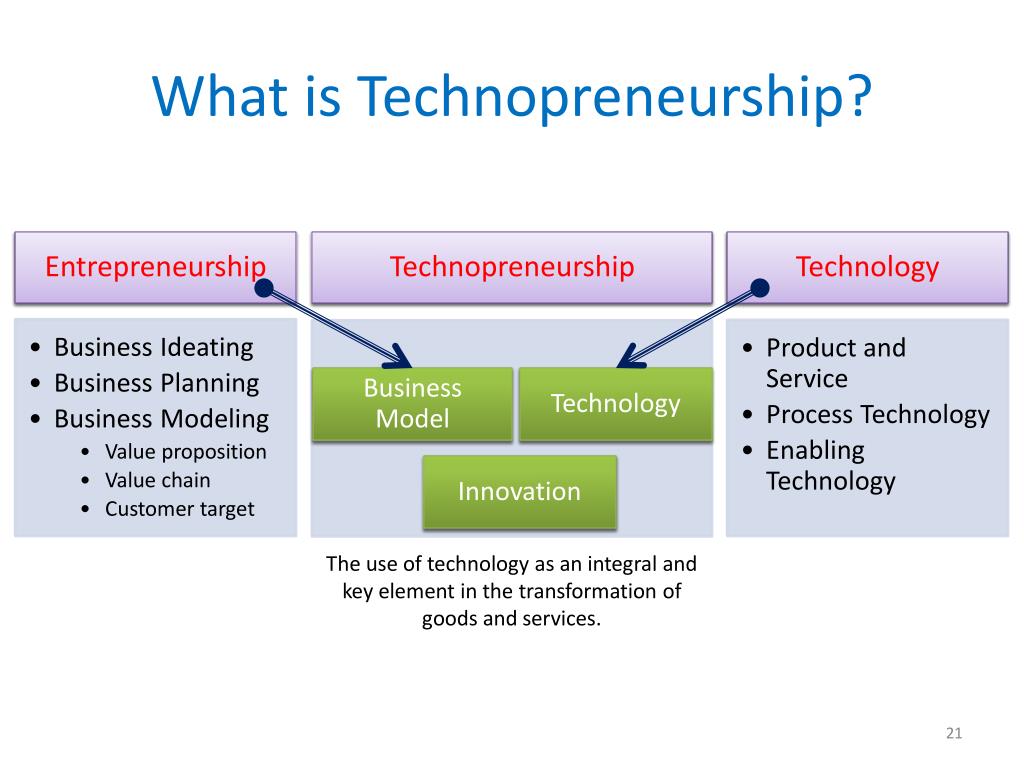
Emergence of Technopreneurship
Entrepreneurship, in its traditional sense, revolves around identifying opportunities, creating ventures, and managing resources to generate profit. It encapsulates a broad spectrum of industries and business types, emphasizing risk-taking and innovation as key drivers of success. On the other hand, technopreneurship, a subset of entrepreneurship, intertwines technology with entrepreneurial endeavors. It focuses on leveraging technological innovations to develop and scale businesses.
Key Differences
Aspect | Entrepreneurship | Technopreneurship |
| Focus | Broad spectrum of industries and ventures. | Primarily technology-based products or services. |
| Innovation Emphasis | May or may not heavily focus on technological innovation. | Centrally driven by technological innovation. |
| Risk Management | Risks associated with market, finance, operations, etc. | Risks include technological advancements, market shifts, etc. |
| Market Reach | Can target various markets irrespective of technology. | Often targets niche or tech-savvy markets initially. |
| Resource Requirements | Varied resources, not solely technology-centric. | Emphasis on tech infrastructure, R&D, and expertise. |
| Growth Potential | Growth is not exclusively tied to technological advancements. | Growth highly reliant on continuous tech innovations. |
| Speed of Change | Adaptation to change might be slower in non-tech sectors. | Rapid adaptation due to fast-paced tech advancements. |
| Scalability | Scalability might rely on traditional methods and strategies. | Scalability often leverages technology for rapid scaling. |
Scalability and Global Reach
The primary distinction lies in their innovation focus. While entrepreneurship spans various sectors, technopreneurship heavily relies on technological innovations as its core foundation. Moreover, the nature of risk differs; traditional entrepreneurship involves market risk, whereas technopreneurship encompasses technological and market risks simultaneously.
In addition, their approaches to market penetration vary. Traditional entrepreneurs tend to focus on existing markets, whereas technopreneurs often create new markets or disrupt existing ones with innovative technology-driven solutions. Furthermore, scalability and global reach differ significantly; technopreneurship, with its technological advancements, often has a higher potential for rapid scalability and global impact compared to traditional entrepreneurship.
Overlapping Aspects
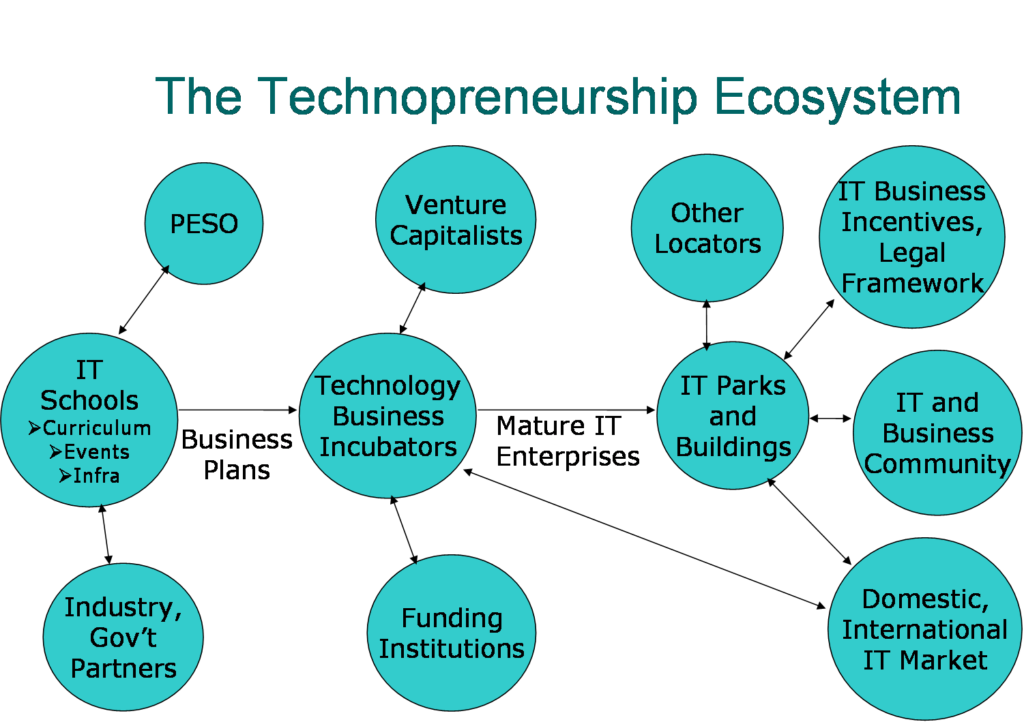
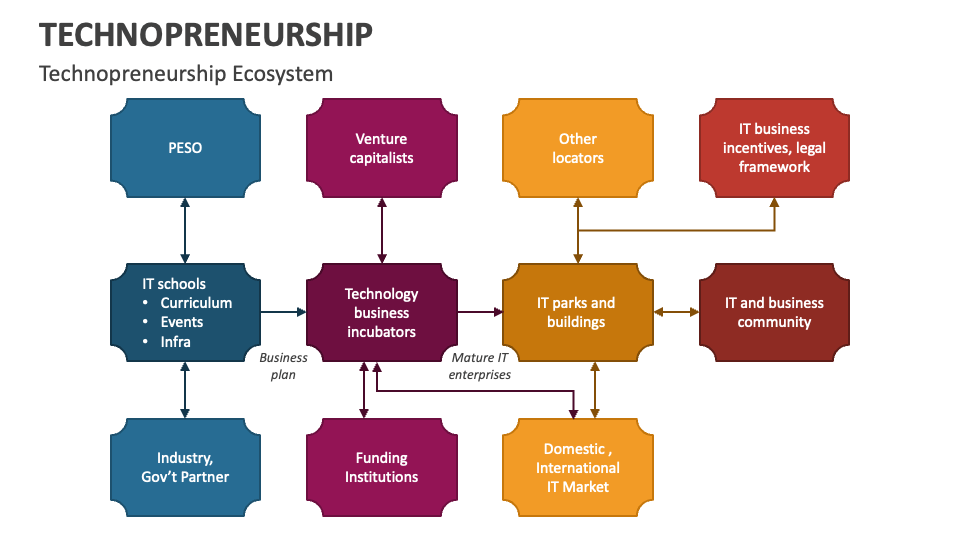
Adaptability and Flexibility
However, despite their differences, both paths share certain commonalities. They both require an entrepreneurial mindset characterized by creativity, resilience, and a vision for growth. Additionally, adaptability and flexibility are vital traits for success in both arenas.
How to become an Entrepreneur?
Becoming an entrepreneur requires a combination of mindset, skills, and actions. Here’s a concise guide to get started:
1. Identify Your Passion and Idea
- Reflect on your passions, interests, and problems you’d like to solve.
- Brainstorm ideas that align with your skills and market demands.
2. Conduct Market Research
- Analyze the market for your product or service.
- Understand your target audience, competitors, and industry trends.
3. Develop a Solid Business Plan
- Outline your business goals, target market, revenue streams, and marketing strategy.
- Create a roadmap for the first few years of your business.
4. Acquire Necessary Skills and Knowledge
- Learn continuously about business management, finance, marketing, and leadership.
- Develop resilience, adaptability, and problem-solving abilities.
5. Build a Network
- Connect with mentors, advisors, and other entrepreneurs.
- Network within your industry to gain insights and potential partnerships.
6. Start Small, Iterate, and Adapt
- Launch a minimum viable product (MVP) to test the market.
- Gather feedback and iterate your product or service based on customer responses.
7. Embrace Risk and Persistence
- Understand that entrepreneurship involves risks; be ready to face failures and learn from them.
- Stay persistent, maintain focus, and adapt to changing circumstances.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while entrepreneurship and technopreneurship share common ground in their entrepreneurial spirit, their divergence lies in their focus on technology, risk nature, market approach, and scalability. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for aspiring entrepreneurs to carve their paths effectively in the evolving landscape of business and techn.
FAQs
Technopreneurship heavily integrates technology but also requires a strong business foundation and innovation mindset for success.
Yes, a traditional entrepreneur can transition by integrating technological innovations into their business model or creating new ventures centered on technology.
Technopreneurs face a different set of risks that include technological and market risks alongside conventional business risks.
Both entrepreneurship and technopreneurship drive economic growth by creating job opportunities, fostering innovation, and contributing to market competitiveness.

